Roughness texture
In short, roughness texture to roughness scalar setting is, what base color texture is to base color scalar setting.
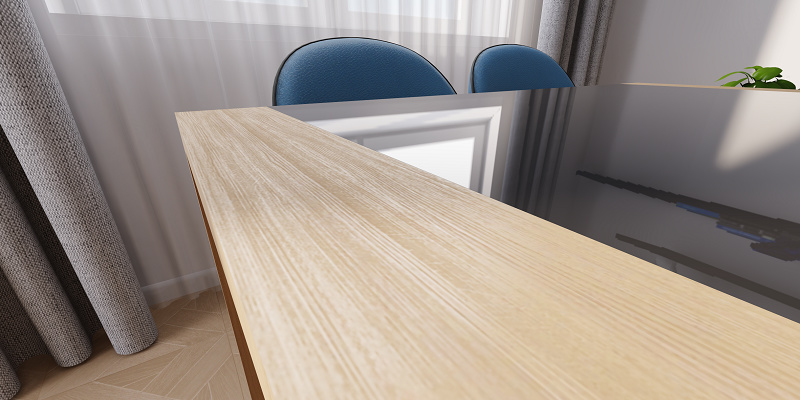
A roughness texture allows you to vary roughness within one material, so to make a single surface reflect light non-uniformly. For example, you can see the effect of using a roughness texture on the oak part of the table below.
(certain areas are more reflective, and others are less reflective)
A pure black color (0, 0, 0) of the roughness texture corresponds to scalar roughness setting = 0, pure white color (255, 255, 255) corresponds to roughness = 1, with grey colors in between corresponding to roughness values between 0 and 1.
In most cases, a roughness texture is created based on the base color map using such image operations as: desaturate (convert image to greyscale), negate or brightness & contrast (levels).
Below you can compare a cropped and zoomed in base color oak texture used for the table and a corresponding fragment of the roughness texture.


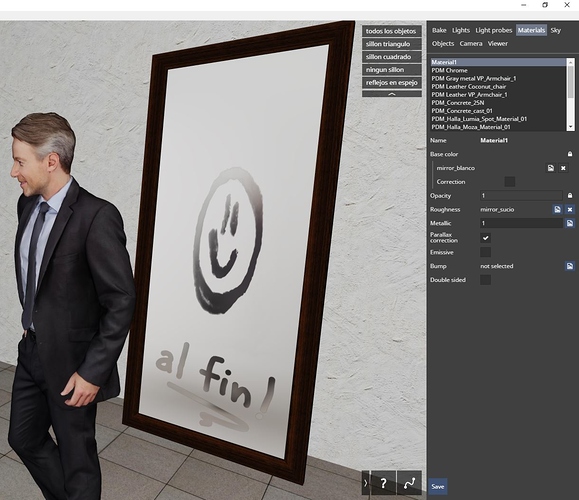
Metallic texture
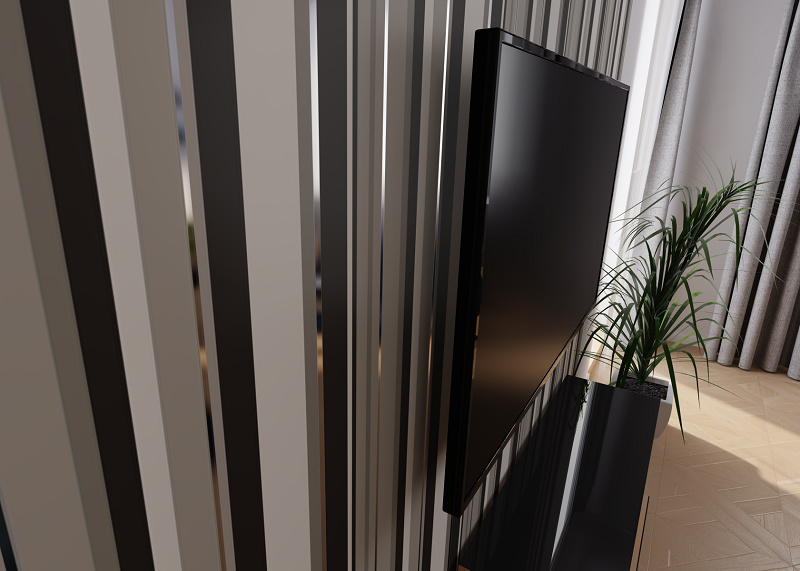
Metallic texture is used to vary metallicness within one material. For example, you can see the effect of metallic texture on the wallpaper below.
With metallic texture, a pure black color (0, 0, 0) of the texture corresponds to scalar metallic setting = 0, pure white color (255, 255, 255) corresponds to setting to metallic = 1, with grey colors in between corresponding to values between 0 and 1.
Below you can compare the base color wallpaper texture used in the above example and the corresponding metallic & roughness textures (roughness given for completeness):

base color

metallic

roughness
Bump texture
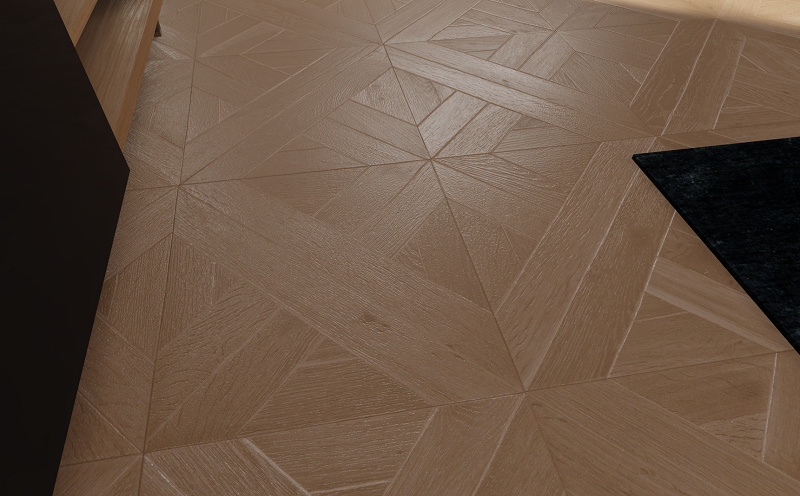
Bump texture is used to model bumps and slits in a surface. For example, you can see the effect of a bump texture on the floor below.
With bump texture, a pure black color (0, 0, 0) corresponds to a deepest slit in the surface, a pure white color (255, 255, 255) corresponds to a highest bump in the surface, medium grey (127, 127, 127) corresponds to regular surface height (neither a slit nor a bump). You can use greyscale values in between to vary slit depths and bumps heights. The overall bump intensiveness for a material is controlled with the Bump scale setting in the editor.